January 2026 – Edition 05
Cataylsts of Change
Building Digital Pathways to Employability at Scale
Anudip Foundation
As India’s labour market rapidly shifts towards digital and AI-enabled roles, preparing underserved communities for meaningful employment has become urgent. For organisations working in digital skilling and livelihoods, scale alone is no longer sufficient. What matters equally is relevance, quality, and the ability to guide learners from enrolment to employment with consistency and care. Anudip’s digital transformation journey offers a compelling example of how technology can be strategically deployed to meet this challenge at scale.
The Organisation and Its Mission
Founded in 2007, Anudip works to create sustainable digital livelihoods for individuals from underserved communities by equipping them with market-aligned digital skills. Operating across 22 states in India, the organisation has reached more than 500,000 learners over time, with a strong emphasis on employability outcomes rather than training in isolation.
As Anudip expanded its geographic footprint and diversified its program offerings, it became clear that existing systems and manual processes were no longer adequate. Scaling impact now required a digital framework capable of managing complexity without diluting quality.
The Challenge of Scale and Fragmentation
Anudip’s operations span the entire learner lifecycle from mobilisation, enrolment, training delivery, mentoring, assessments, and job placement. Over time, these functions came to be managed through disconnected tools and manual workflows. Learner data was fragmented across systems, real-time visibility was limited, and actionable insights were often delayed.
This fragmentation affected both learner experience and organisational efficiency. Trainers lacked timely data to personalise support, managers struggled with central oversight, and job matching could not keep pace with market demand. To scale responsibly, Anudip needed an integrated, learner-centric digital ecosystem.
Building a Hybrid Digital Ecosystem
Rather than adopting a single off-the-shelf solution, Anudip embarked on a structured digital transformation grounded in its programmatic needs. The organisation built a hybrid digital ecosystem combining centralised systems, learning platforms, and AI-enabled tools.
A Computerised Management Information System (CMIS) was introduced to streamline enrolment, documentation, and learner records, creating a single source of data across centres. This was complemented by a Learning Management System (LMS) that standardised content delivery, tracked learner progress, and ensured consistent training quality.
To strengthen the critical transition from training to employment, Anudip developed JD–CV Match, a tool that significantly accelerated the matching of trained candidates with suitable job opportunities. Virtual interview modules and AI-enabled assessment and support tools further enhanced employability readiness. Real-time dashboards provided trainers and managers with actionable insights, enabling faster decisions and more responsive learner support.
Managing Change and Driving Adoption
A defining feature of Anudip’s approach was its focus on change management. Technology adoption was not treated as a top-down mandate. Trainers, centre heads, and operational teams were actively involved in design, testing, and rollout to ensure tools aligned with on-the-ground realities.
Implementation followed a phased approach, allowing teams to adapt gradually and provide feedback. Anudip also made deliberate ‘build vs buy’ decisions, developing tools in-house where domain expertise was strong, and partnering externally where specialised capabilities were required. Funders were engaged as long-term partners, with several supporting multi-year investments in digital infrastructure.
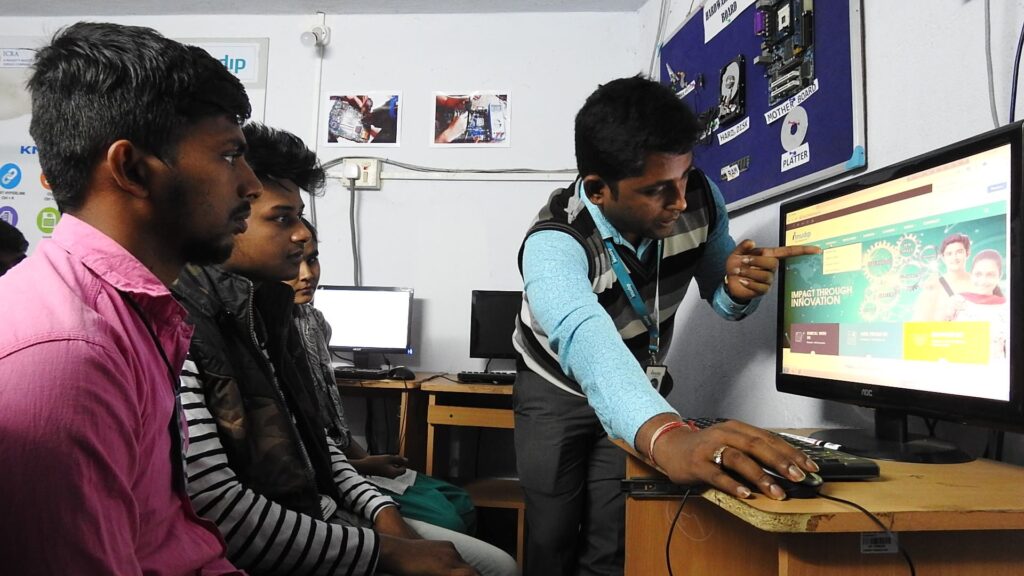

Outcomes that Strengthened Employability
The results of the transformation were substantial. Anudip achieved placement rates of over 70% percent for eligible learners, while JD–CV Match reduced job-matching timelines by nearly twenty times. More than 90 centres were digitised, enabling central visibility without undermining local engagement.
Content creation cycles shortened, learner feedback participation increased, and data-driven decision-making became easier across teams. Crucially, technology enhanced rather than replaced human interaction, allowing trainers and mentors to focus on personalised guidance where it mattered most.
Key Lessons
The Anudip case highlights several lessons for organisations working in skilling and employability in the social sector.


Copyright © 2026 India Leaders For Social Sector
